The proliferation of sophisticated agentic AI capabilities is rapidly reshaping the enterprise landscape, moving beyond simple automation to enable autonomous, goal-driven execution of complex business processes. However, leveraging this potential on a scale requires more than just technical deployment; it demands holistic organizational preparation.
Microsoft survey identifies four types of AI maturity
To assess organizational readiness, 500 decision-makers and influencers across 13 countries and 16 industries self-evaluate by answering 25 questions grouped into five main pillars.
Five areas of readiness for the AI agent
Microsoft divided all pillars into two: strategic (including Business & AI Strategy and Business Process Mapping) and execution (Technology & Data, Org Readiness & Culture, Security & Governance).
The following sub-items were the theme of the 25 self-evaluating questions, with each column representing one pillow.
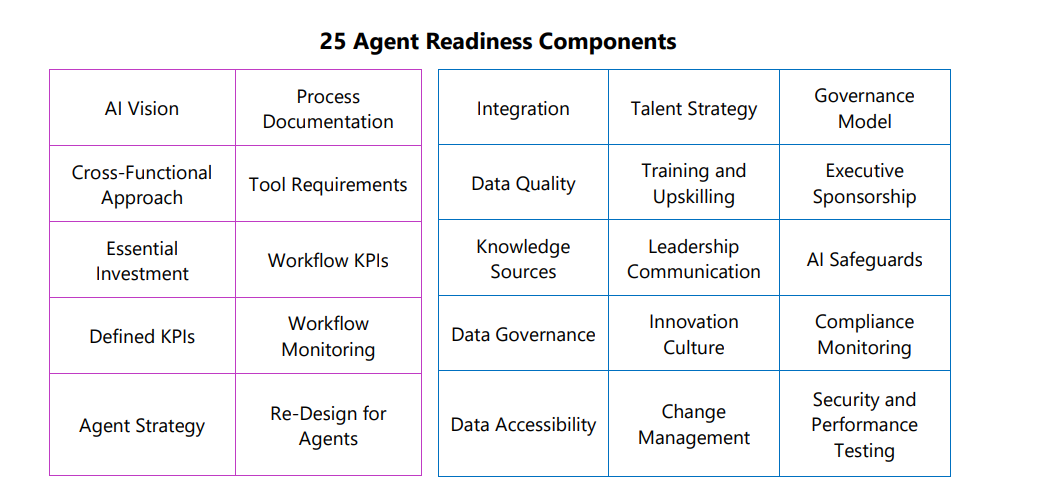
picture from Microsoft whitepaper
Pillar One: Business and AI Strategy
This initial pillar stresses that every initiative involving agentic AI must originate from specific strategic business objectives and quantifiable key performance indicators for the organization.
Key Practices:
Pillar Two: Business Process Mapping
The ultimate effectiveness of an AI agent is inherently constrained by the quality and precision of the business process it is programmed to execute.
Key Practices:
Pillar Three: Technology and Data
This pillar addresses the need for a strong technical and data foundation to enable the scalable, enterprise-wide deployment of agents.
Key Practices:
Pillar Four: Organizational Readiness and Culture
Organizational preparedness and culture are essential for realizing the full advantages of AI, as people, not merely agents, are the driving force behind transformation.
Key Practices:
Pillar Five: Security and Governance
The final pillar is dedicated to embedding strict governance and protection measures early on to ensure safe, enterprise-wide adoption and mitigate risks such as security breaches or loss of public confidence.
Key Practices:
Power of all five pillars
Ultimately, successful adoption of agentic AI is not about isolating technology; it is about merging clear strategy (Pillar One) with refined processes (Pillar Two), a resilient technical foundation (Pillar Three), an embracing culture (Pillar Four), and airtight security (Pillar Five). By consistently addressing these interconnected areas, organizations can reliably unlock the full transformative potential of agentic AI, ensuring that agents are deployed safely, securely, and with maximum business impact.



















