In today’s highly competitive, data-driven supply chain environment, new, more sophisticated maintenance strategies are essential. The foundation for this transition is a flexible, cloud-based platform like Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management. This solution provides the necessary tools to move maintenance from a necessary cost center to a proactive, data-driven enabler of supply chain resilience and operational excellence.
Modern VS Traditional Maintenance Model
Traditional maintenance mainly depends on reactive and preventive methods—fixing equipment only after failures or during scheduled checks. This often results in downtime, reduced productivity, additional costs such as rush repairs and overtime, safety hazards, and damage to reputation. Modern strategies combine these traditional techniques with remote monitoring, predictive analytics, and cognitive maintenance. This holistic approach aims to prolong asset lifespan, boost throughput, improve quality and uptime, lower expensive machinery failures, and promote safer working conditions.
Dynamics 365 Decision for Supply Chains
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management provides the essential foundation and flexibility to transition maintenance to the cloud while supporting any current approach. It enables a shift from reactive to proactive maintenance, facilitating real-time, data-driven decisions and strengthening supply chain resilience.
Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management’s features promote proactive maintenance by integrating multiple technologies. IoT sensors track various conditions to gather vital data, leading to decreased costly downtime and improved uptime and throughput.
Mixed Reality is incorporated via Dynamics 365 Guides, utilizing HoloLens to deliver hands-free work instructions directly in a worker’s view. This allows remote experts to assist and train employees swiftly, enhancing productivity.
For advanced data analysis, machine learning algorithms analyze extensive maintenance data to recognize patterns. This allows the system to learn, act proactively, save time, and enhance safety by identifying maintenance problems before they occur.
Finally, Business Intelligence tools examine and assess the entire supply chain, providing insights that support better decision-making, help identify potential risks, and build a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing overall success.
5 Maintenance models
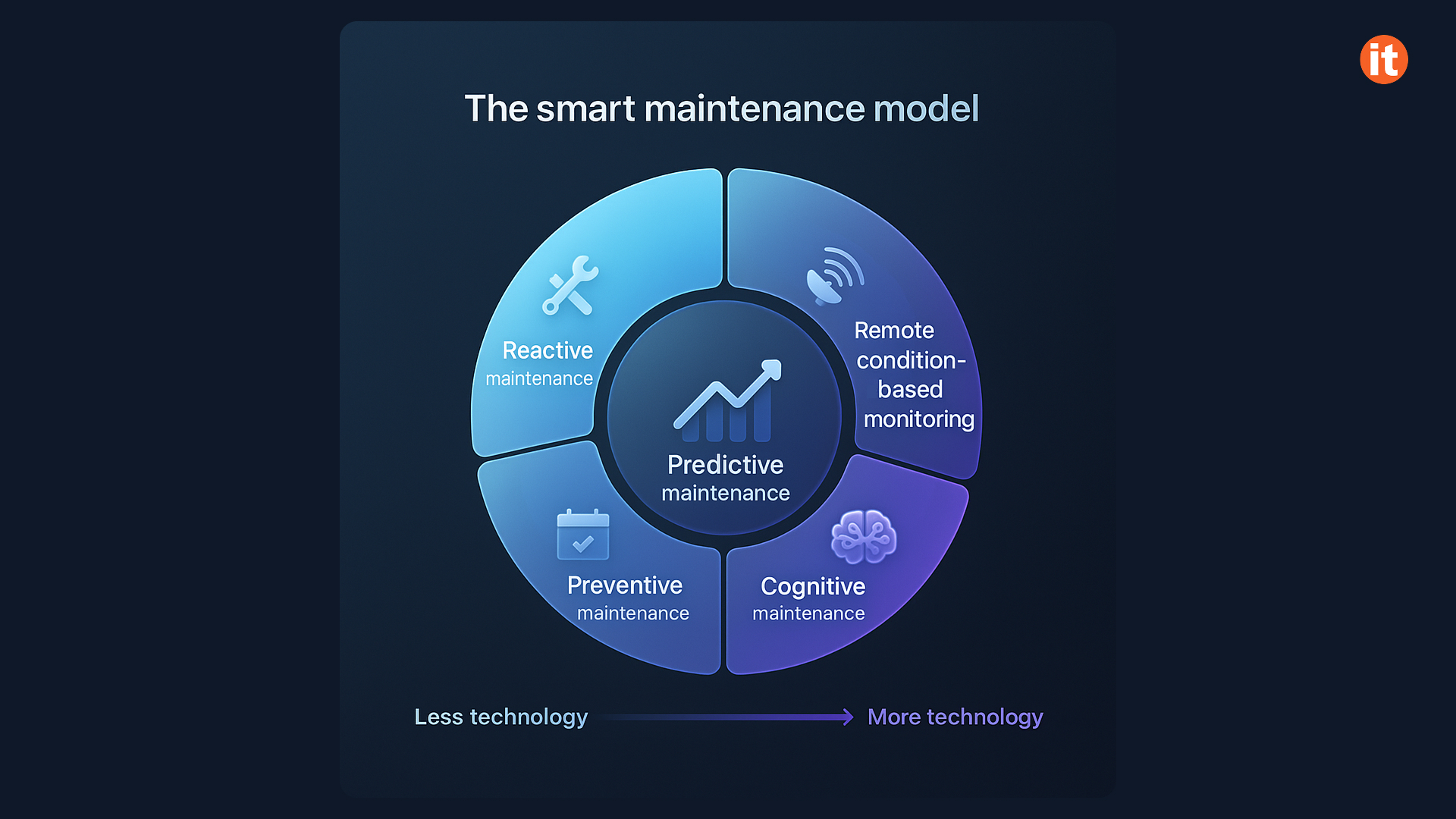
Reactive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance usually means fixing or replacing equipment only after it breaks or shows signs of wear. This method works best for supply chain parts that are not critical and won’t cause major disruptions if they fail. It’s especially suitable for small, low-cost, redundant items that have little effect on overall operations. To be effective, workers should be well-trained to recognize issues promptly and have access to a stock of spare parts to maintain smooth system operation.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is a proven, data-driven approach that focuses on proactively repairing and maintaining equipment to avoid failures. It supports other maintenance strategies and is especially important for heavily used, costly, or complex items critical to the supply chain. Successful implementation depends on a carefully planned schedule integrated with the supply chain timeline, selecting between time-based or usage-based techniques for each asset, and having a dedicated team to manage scheduling and inventory effectively.
Remote Condition-Based Monitoring
This method enhances preventive maintenance by employing wireless sensors that relay data to a maintenance manager, effectively turning machinery into Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Instead of adhering to a fixed schedule, maintenance is carried out based on sensor data indicating necessity, such as when vibration reaches critical thresholds. This approach lays the groundwork for more sophisticated maintenance techniques. It is particularly suitable for equipment that experiences random failures without obvious patterns, does not undergo wear, and monitors parameters like vibration, temperature, pressure, or flow. Essential components include sensors, a data collection and notification platform or dashboard, and employee training to manage work orders.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance improves smart maintenance by using a digital feedback loop that forecasts equipment failures from both historical and real-time data. Accurate predictions rely on high-quality data and the seamless integration of data and technology to schedule maintenance effectively and prevent failures in advance. This method works best when a company promotes a proactive maintenance culture, equipment experiences wear, spare parts are accessible, and failure patterns are well understood. Implementing this successfully involves thorough staff training and collaboration with a technology partner to install sensors, data collection systems, dashboards, and analysis tools.
Cognitive Maintenance
Cognitive maintenance stands as the highest tier in the smart maintenance hierarchy and is the most technologically sophisticated approach. It can “think ahead” with greater accuracy than predictive models. For instance, when a sensor reports low pressure, the system combines historical data, maintenance guidelines, and expected performance to forecast a specific part’s failure, automatically orders a replacement, and issues a work order.
This approach not only ensures optimal equipment performance but also enhances workforce efficiency, production output, and customer satisfaction by reducing downtime. It is particularly ideal for companies with high production volumes, extensive equipment usage, or those already engaged in digital transformation. Recognizing the importance of intelligent, integrated systems for business continuity, such companies find this approach beneficial. Like predictive maintenance, it requires thorough training and collaboration with a technology partner to integrate all components successfully.
Evolving Beyond Traditional Maintenance
The journey from a traditional reactive or simple preventive maintenance program to a cognitive model represents the ultimate evolution of supply chain resilience. While reactive and preventive methods remain foundational, particularly for non-critical assets, the modern competitive landscape demands the adoption of remote condition-based monitoring, predictive maintenance, and the highly sophisticated cognitive maintenance approach.
Platforms like Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management are instrumental in making this transition possible. By seamlessly integrating IoT data, Mixed Reality assistance, machine learning algorithms, and Business Intelligence tools, organizations can shift from merely fixing problems to proactively forecasting and preventing failures. This data-driven, intelligent framework not only ensures optimal equipment performance and maximum uptime but also enhances workforce efficiency, bolsters safety, and significantly strengthens the entire supply chain against disruption.
Adopting this comprehensive, modern maintenance strategy is no longer a luxury but a strategic imperative for businesses aiming for high production volumes, extensive equipment usage, and continuous digital transformation. The maintenance model for today is intelligent, integrated, and completely proactive, positioning companies for long-term operational success and superior customer satisfaction.

















